The Data Observation Toolkit: An open source tool to increase trust in public health data
By Mignonne Fowlis, Senior Manager, Product & Programs, DataKind
Data collected by frontline health workers (FHWs) is essential to a robust healthcare delivery system, as is the quality of the data. Missed vaccinations, inadequate maternal care, delayed disease response – these aren’t just statistics, they are the devastating consequences of poor data quality in frontline health systems.
If data collected by FHWs is inaccurate or inconsistent, or the data is mistrusted by decision makers, it undermines the entire healthcare delivery system, leading to poor health outcomes and inequities in healthcare delivery. High-quality care for communities requires improving confidence in FHW-collected data, ensuring it reliably informs patient care, shapes policies, and guides decisions.
What if we could automatically detect these data quality issues before they impact patient care?
An online tool to increase quality and trust of health data
Enter the Data Observation Toolkit (DOT), a community-informed, open-source software and certified Digital Public Good designed to automate data quality checks, detect anomalies, and enhance trust in health data. DOT stands out as a platform-agnostic, cost-effective, and user-friendly solution, designed to meet the needs of governments, NGOs, and frontline health organizations operating in diverse technical environments. For more information on how DOT works, see here.
From Uganda’s maternal health services to Lesotho’s specimen transport systems, DOT is demonstrating how automated data validation can strengthen healthcare delivery in resource-constrained settings. Below, we share three case studies that illustrate DOT’s real-world impact and its potential for broader adoption.
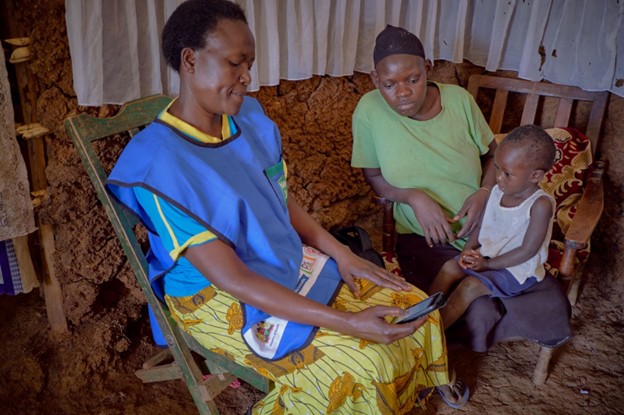
Improving Maternal Healthcare Service Delivery in Uganda
In 2024, for Uganda’s Lamwo and Ntungamo districts, DOT was integrated into the Ministry of Health’s electronic Community Health Information System (eCHIS), serving over 684,000 people, with training provided for approximately 500 Village Health Teams. During this time, DOT automatically checked 5.3 million data rows, surfacing critical issues that would have otherwise gone unnoticed.
- Nearly 8,000 pregnancies with fewer than four antenatal care visits were flagged for follow-up
- Multiple pregnancy outcomes incorrectly recorded under single pregnancy IDs were detected and revised
- Missed follow-ups and data duplication issues were caught early
These insights enable FHWs to provide more reliable maternal care services, directly improving health outcomes in their communities and building confidence in FHW-collected data.
Its broader application within Medic’s Community Health Toolkit—a platform utilized by over 130,000 frontline health workers across 15 countries—has further streamlined data quality practices, supporting better health outcomes at scale. As of February 2025, DOT is live and fully operational in Uganda. Across the border, a DOT trial is underway in Kenya with the Ministry of Health.
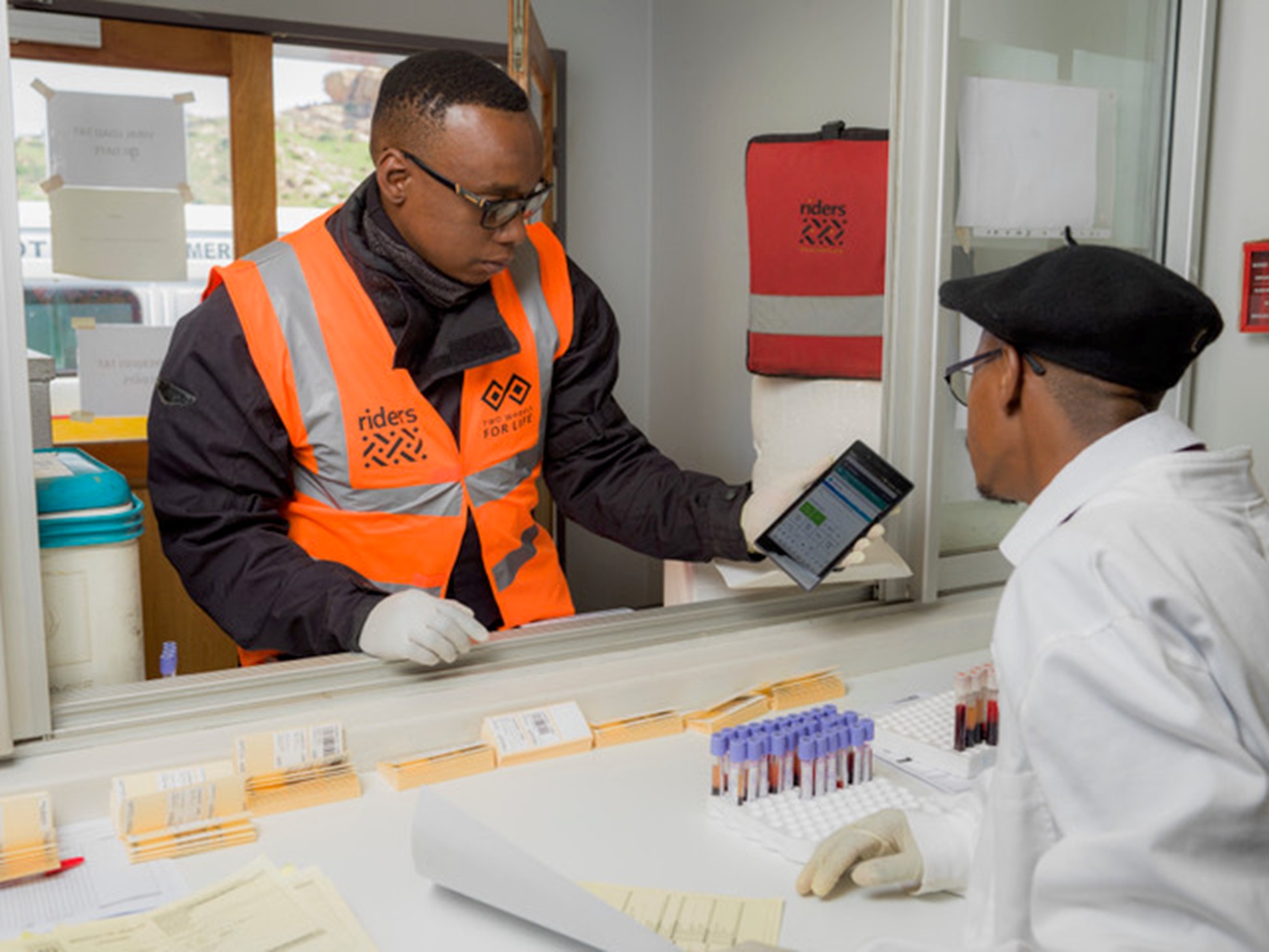
Transforming Specimen Transport in Lesotho
In Lesotho, DOT is currently deployed by Riders for Health (Riders), a social enterprise that provides transport for healthcare delivery. Their challenge: managing quality control of data for nearly half a million specimens being transported annually for infectious disease monitoring, across ten districts serving 2.2 million people. Riders had previously relied on manual data quality check processes – an approach prone to errors and inefficiencies.
DOT’s implementation enabled Riders to automate quality checks. Custom tests tailored to Riders’ operational needs, such as time-bound data checks, were developed, enabling faster identification and resolution of discrepancies. A custom cloud-hosted solution was developed to handle spreadsheet-based data, making DOT even more accessible to organizations without complex database systems.
Building on the success in Lesotho, plans are underway to expand DOT’s use to Riders’ operations in The Gambia, Malawi, and Nigeria.
Strengthening Global Vaccine Delivery Systems
Accurate data for vaccination programs can mean the difference between achieving or missing vaccine immunization targets.
In partnership with Gavi and stakeholders across the Gavi Alliance and Innovation for Uptake, Scale, and Equity (INFUSE) Pacesetters, DOT was implemented as a prototype on global immunization datasets. This deployment demonstrated its ability to swiftly identify anomalies, enabling rapid remediation and enhancing the accuracy and reliability of vaccine data. See the demo and read the report here.
This successful proof-of-concept deployment highlighted the broader potential of AI and data science tools in global health. Building on these promising results, plans are underway to develop a scaling roadmap, enabling Gavi and its partners to harness these digital innovations for equitable vaccine access and immunization goals.
Key Lessons Learned
Our work with frontline health organizations has revealed three critical insights about improving data quality in resource-constrained settings:
- Automation is indispensable: manual data quality checks simply cannot reach scale and they often miss critical issues that directly affect patient care.
- Health organizations require flexible tools that adapt to their reality—whether working with basic spreadsheets or complex databases.
- Success hinges on local ownership; when FHWs and health system managers can easily identify and address data quality issues themselves, they’re far more likely to maintain high data standards over time.
At DataKind, success means developing data science and AI solutions that are widely adopted and contribute meaningfully to addressing sector-level challenges. We design our tools to be accessible, flexible, and reusable, principles which were embedded into DOT’s development.
Through our deployments, we’ve seen firsthand how data quality challenges undermine decision-making across multiple sectors. These experiences reinforce the need for platform-agnostic, sector-agnostic solutions like DOT to build trust in data and drive informed decision-making at scale.
Get Involved
If you’re working on an initiative to get insights from your datasets and improve data quality, check out DOT on the Digital Public Goods site, on GitHub, or write to us at partners@datakind.org. You can also connect with us in-person later this year at the Global Digital Health Forum in Nairobi!
DOT was developed by DataKind in partnership with Medic as the first solution to be advanced under DataKind’s work Frontline Health – a funded program to research, design, and build reusable, accessible, and flexible AI and data science tools that strengthen frontline health systems. This initiative was made possible through the generous support and partnership of Wellcome and Johnson & Johnson Foundation, each of whom played critical roles through key phases in the development and deployment of DOT.