Where are you from?
I’m originally from Israel, specifically a city south of Tel Aviv called Rishon Le Zion.
What did you do before working at TechChange?
Before I worked at TechChange, I worked as an Animator/After Effects Compositor on a few different children’s cartoons. The shows were produced either in Israel, or in Europe. I worked both in a production studio environment and I spent some time traveling and working where ever I had a stable internet connection and a desk.
How did you hear about TechChange?
I heard about TechChange through a job posting on indeed.com.
What exactly do you do at TechChange? What does a typical day look like for you?
I coordinate the work of our amazing creative team, with the vision of the instructional design team and provide feedback and guidance for different projects. My typical day would start by talking to my team, getting their input on current projects, checking their progress and setting goals for the day. Followed by answering clients and team emails. After that I would go into either storyboarding, drafting a concept note for a project, editing video boards (for animation), animate, figuring out next steps for larger projects, hop on check-in calls with clients or any other task that requires my input. At the end of the day I would make sure that the creative team has delivered completed tasks, check in with Nick or Chris on long term deliverables and plan my next day. The job is pretty diverse and requires a lot of long term planning, as well as attention to details. The things I always try to ask myself are: Are we on schedule? Are we improving? Are the team members in the loop?”
How did you get into animation?
As a kid, I was (and still am) a geek that spent a lot of time indoors watching TV and movies – especially cartoons and Disney movies. With heroes like Bugs Bunny, Spiderman and the Genie, I was amazed by the power of animation. I couldn’t believe that there were people out there creating visual representations for stuff that I thought only existed in my head. Growing up, I went to an engineering high school, and my sense for design and animation wasn’t very encouraged. After I finished my mandatory military service, my girlfriend at the time (now my wife) sent me a link to the animation department of Bezalel Academy of Arts and Design in Jerusalem. I had no idea that a career in animation and design was even an option, but I told myself that if I get in, I’ll go for it. I applied and some how got through the tests. The first two years were very hard, but even after a lot of failures I couldn’t give up, because my drive to animate and draw kept growing as school was getting harder and harder. 4 years after graduating, I look back and I know that taking that chance was one of the best decisions I ever made.
What is the most important lesson you’ve learned in creating animations for international development and social change?
The most important lesson in international development that I’ve learned is that there is a lot of room for creative thinking. Coming from a design background, I try to approach animation projects with a clean slate and do a lot of exploration. I’ve learned that this approach can applies to international development-related work as well, especially when explaining data-intensive concepts in visually compelling ways that make it easier to understand.
How do you keep up with the latest developments in animation/multimedia technology and trends?
A lot of web browsing. I have a Google News feed that keeps me updated on these issues, as well as colleagues who post interesting articles on Facebook and Twitter.
What do you love most about working at TechChange?
The people. This is by far the best team I’ve ever had the chance to work with. There’s a wonderful environment here, amazing energy, and hard working individuals.
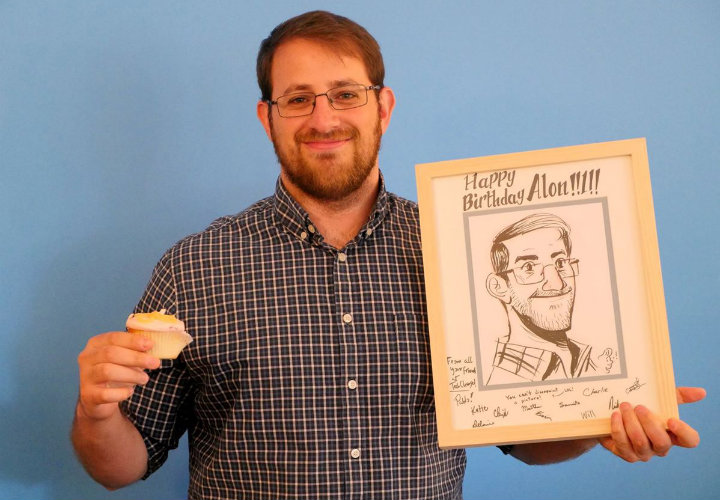

Alon with his birthday gifts from TechChange: cupcakes and a sketch of himself made by his co-worker Pablo
What is your favorite TechChange moment so far?
After almost two years of living in the US, I finally got to have a proper Halloween office party. In the party I had the privilege to participate in a short intellectual experiment called: “Between Two Nerds”. Thanks to Nick Martin, Pablo Leon and Charlie Weems, it turned out to be one of the best productions I ever took part in.
What do you do when you’re not at TechChange?
I enjoy spending time with my wife, watch movies, read comics/books, work on personal animation/design projects, hike, play PC games, and hangout with friends.
If you had to direct someone to the best place to eat in D.C. where would it be?
Busboys and Poets. Great food, awesome atmosphere.
Does Alon’s job sound like your dream job? Apply to our Animator/Videographer position here.