Featured image credit: Andy Miah Creative Commons License
Today we had the opportunity to chat with Steve Ollis of D-tree International, who will be a guest expert for our Mobile Phones for Public Health course. Below, he discusses his experience working in the mHealth field!
Can you tell us about your background and experience in mHealth?
I came into mHealth and global health in a somewhat non-traditional way. I actually started off as an accountant and management consultant with BearingPoint, working with various US government military branches on their accounting systems. I moved into IT consulting with a focus on program management for the next six years, working at progressively smaller companies, bringing web applications to state and federal agencies and addressing issues like help desk, user training and support, and change management needed to introduce and sustain new applications in large organizations.
My career in mHealth and global health started with a few short volunteers stints in Kenya and South Africa followed by a position with the Clinton HIV/AIDS Initiative (now Clinton Health Access Initiative) for two years in Tanzania, working in pediatric HIV, commodities, lab systems and Prevention of Mother to Child (PMTCT) programs.
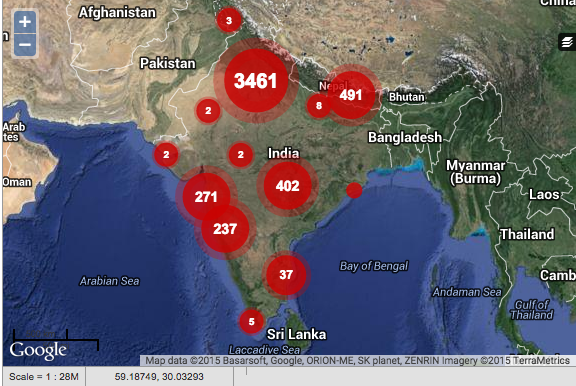
With this exposure to the global health world and my background in information technology, I was intrigued by the possibility of working in the mHealth space and joined D-tree International in Tanzania six years ago. I have been fortunate to work on cutting edge mobile decision support tools focusing on design, development, deployment and support. I have seen projects grow from 1-2 facility to over a hundred facilities, and 5-10 community health workers to thousands of health workers. Over the years I have also seen a dramatic price drop for Android phones from $650 t0 $80. I have worked in Tanzania, Benin, Malawi, Kenya, Sri Lanka and India as part of small and large teams, and have worked at both the community health worker and Ministry of Health levels.
How is mHealth incorporated to your work currently?
D-tree International is a health NGO that uses mobile technology to improve the care provided by frontline health workers. We are working at the government, donor, implementing partner and ground levels to develop applications and systems that support decision makers at all levels, from the community health worker and nurse level to health systems supervisors. We focus on providing mobile decision support tools to health workers, and creating health systems to provide them adequate support. We use mobile technology to improve health outcomes by developing supervisory applications, dashboards, mobile money integration for transport, vital events tracking, and point of care diagnostics.
Why do you think mHealth is important / what impact can learning about the use of mobile phones for public health have on development projects?
It is amazing to think about how we can do things more effectively and efficiently using mobile devices, including data collection, applications, closed user groups and telemedicine. At a higher level it is useful to think about how these innovations can be introduced, scaled and supported in order to create significant impact and change.
What are your thoughts on the future of mHealth, and where you think this field is heading?
We’ll see continuing availability of smartphones at all levels of society and the prices will come down further. The price of data and sms will also be reduced and connectivity will increase at greater bandwidth. These forces will allow for increasingly complex mHealth systems to be developed where data, images and video may be able to be shared even in the most remote areas. Point of care diagnostics will continue to evolve, where the prices and power requirements for certain tests will drop to a point that they become more feasible to deploy at the community level. Mobile money, vouchers and mobile insurance will also play a role as the health workers and clients become more familiar with their use in their day to day lives. Power and lack of unique identifiers will remain significant challenges, but innovative solutions should be available soon in areas where we work.
We believe mHealth skills have the potential to make a huge impact in your work. Why do you think taking this class is important, and who would you recommend it to (public health professionals, field workers, etc etc).
This course provides a great overview of different types of mobile technologies and mHealth projects in addition to providing a unique opportunity to connect with a community of implementers and experts in the field. It will also provide some guidance around processes and structures required to include a successful mHealth component to a project. I am a firm believer in the potential of mHealth to radically transform the current state of healthcare. Everyone from policy makers to healthcare workers need to think about how we can use these tools to save lives and help people live healthier, happier lives.
Any advice for someone who wants to make a career in mHealth?
There are many opportunities available for people from all backgrounds. There is a need for people not only with health and technology skills, but also with sociology, anthropology, finance and business, project management and analytics skills. I think it’s important to be conversant in the technology, but to keep exploring these other areas which are critical to the work we are all doing to introduce and support game changing innovation in health systems for the good of the communities we serve.
About Steve
Steve is D-tree’s Chief Operating Officer with over 20 years experience in management consulting, information technology and public health. Steve holds a Bachelor’s degree in Finance from The American University and a Master’s in Business Administration in Information Systems and Finance from the University of Maryland. He is also a certified Project Management Professional. Prior to joining D-tree, Steve worked for the Clinton HIV/AIDS Initiative in Tanzania directing programs in Pediatrics, Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission of HIV, and Rural Care and Treatment.