By Lara Henneman, TechChange Special Projects and Storytelling
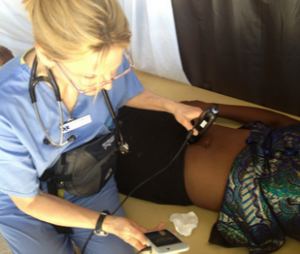
From her work in clinical care and public health in both Benin and the United States, to consulting for the United Nations Fund for Population and Oxfam, Dr. Marlene “Joannie” Bewa’s extraordinary career has been driven by her deep-seated commitment to advancing access to healthcare through innovation. Her personal experiences facing major health complications in her childhood and losing her best friend at 12 years old from the complications of unsafe abortion represent one of her motivations. Leveraging her fifteen years of experience in sexual, reproductive, and maternal health, and digital health, Dr. Bewa founded Benin’s first teleconsultation platform, DOTOH. This mobile application provides real-time consultations in primary care, sexual, and reproductive health for underserved communities including youth, women, and adolescents–groups who often face stigma and geographic barriers in accessing care. D-tree and TechChange are proud to recognize Dr. Bewa as a 2024 Marc Mitchell Award recipient, an honor that will sponsor her attendance at the upcoming Global Digital Health Forum and connect her with one year of valuable professional mentorship from the Global Digital Health Network.
Marc Mitchell Award recognizes digital health innovators
Dr. Bewa is one of two winners of the Marc Mitchell Leadership and Innovation Award, given in memoriam of the Harvard pediatrician and digital health pioneer who founded D-tree in 2004. Dr. Mitchell’s groundbreaking work from Papua New Guinea to Mexico was guided by his passionate belief that all people everywhere should have access to high-quality healthcare, and the award in his honor is now given annually to professionals early in their digital health careers who exemplify that principle. Dr. Bewa’s work founding and leading DOTOH showcases the dedicated resolve and creativity this award is intended to celebrate.
App expands access to vital services for women and youth
In Benin, nearly 20% of adolescents aged 15-19 have given birth, and only 12% of women of any age use a modern contraceptive method. DOTOH, which means “health professionals” in Fon, the most spoken local language in Benin, aims at increasing the uptake of reproductive and preventative health services for women and young adults to aid decision making and family planning. Using the mobile platform available in English and French, users can make appointments, connect online for audio or video consultation for contraception counseling, maternal and child healthcare, family planning, general healthcare, and use the embedded GPS to track surrounding pharmacies.
DOTOH users can also access a complete library of articles on topics related to sexual and reproductive health, as well as primary care– all in a safe, confidential virtual environment. Information, access, consultation, and products are all a critical part of the healthcare services provided by Dr. Bewa’s DOTOH app, and digital technology ensures their reach goes further than ever. The Grand Challenges Canada Stars in Global Health Innovation Award funded this initiative through the Young Beninese Leaders Association (YBLA), an impactful nonprofit organization founded by Dr Bewa in 2010 in Benin, with expertise in health, innovation, and leadership.
An advocate for inclusive, user-centered design
As digital development practitioners, we at TechChange know that how you build things matters. In a recent conversation, Dr. Bewa shared that “women adolescents often face unique barriers to accessing care, particularly in areas where stigma or cultural norms limit their autonomy. Digital health solutions can offer privacy, accessibility, and empowerment, but only when the solutions account for the cultural barriers that limit autonomy.” Through her experiences with DOTOH, Dr. Bewah knows well that it’s vital to design solutions that are deeply rooted in the needs and contexts of users, and built her own app with vigorous testing and co-design with women and youth to ensure the platform was relevant, user-friendly, and responsive.
And she’s looking forward to building this expertise on inclusive digital health initiatives further through participating in the year-long mentorship with the Global Digital Health Network, a 3900+ person-strong networking forum, and at GDHF 2024, where specialized tracks on GESI (Gender Equity and Social Inclusion) and Localization underpin the dynamic agenda. We’re so pleased to welcome Dr. Bewa to the conference as a 2024 Marc Mitchell Award winner.