What does the rise of #YesAllWomen mean for social change?
In our last post on #BringBackOurGirls, we examined whether social media activism could free girls who had been kidnapped in Nigeria. With the rise of #YesAllWomen, it’s worth exploring whether social media can improve the lives of women and men everywhere in shifting social norms around gender.
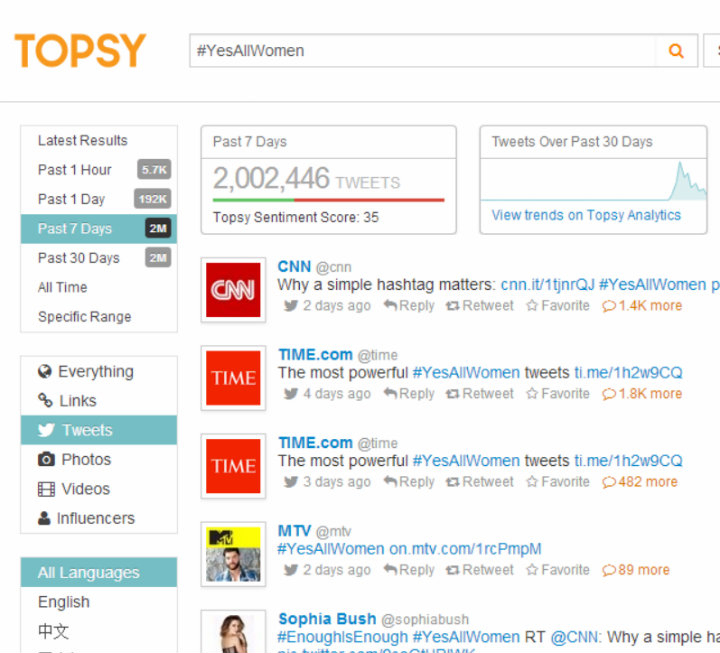
Less than a week after the killing spree at the University of California Santa Barbara, a torrent of more than two million tweets have been shared containing anecdotes, stories, and outcries against misogyny, sexual harassment, and violence against women.
Source: Topsy
Why has #YesAllWomen gained so much media attention? It can be argued that the #YesAllWomen hashtag has built off continuing momentum of other initiatives that have women (and some men) speaking out against misogyny in its many forms. A provocative article from TIME Magazine in April 2014, nearly a month before the UCSB murders, was a critique of the #NotAllMen argument, setting the stage for women to share how sexual harassment and misogyny are frighteningly common experiences that women face on a regular basis. Foreign Policy’s piece on “What do #YesAllWomen and #BringBackOurGirls have in common?” highlights:
“[…]the global Internet has during the last month seen an incredible outpouring of support for the full equality of women. Even if the two hashtags fail to end misogyny and free the kidnapped schoolgirls, they surely represent a step in the right direction in advocating for a better reality for women.”
Here is a heat map visualizing the use of #YesAllWomen hashtag on Twitter, showing the start of the hashtag in the U.S., in comparison to Nigeria, where the #BringBackOurGirls hashtag began.
Related campaigns using the hashtags #everydaysexism and #rapecultureiswhen have both been used in similar efforts to shed light on misogyny, as discussed in CNN’s article on “Why #YesAllWomen took off on Twitter.” Campaigns across U.S. campuses have also been pressuring universities to address sexual assault on campuses, as mentioned in the Chronicle of Higher Education.
What will be the ultimate impact of #YesAllWomen? Will this social media momentum change ingrained cultural norms of sexism across society? It did, at least for Kenneth Curtis, a man who described his reaction to the #YesAllWomen tweets:
“The courageous voices I saw on #YesAllWomen burst my bubble in all the good ways. They shed a light on my ignorance. They also shed a light on the work we men have to do. This is how change happens. Shed a light on the problem. Now let’s rally to fix it.”
But what about the societies where women cannot speak out as openly on social media due to censorship or lack of access to technology? With #YesAllWomen, social media has succeeded again in being a tool for raising awareness on a social issue, but it will continue to be a long journey to shift entrenched cultural norms.
===
Interested in this topic and how social media can be used to create social change? Enroll now in our upcoming Social Media for Social Change course.