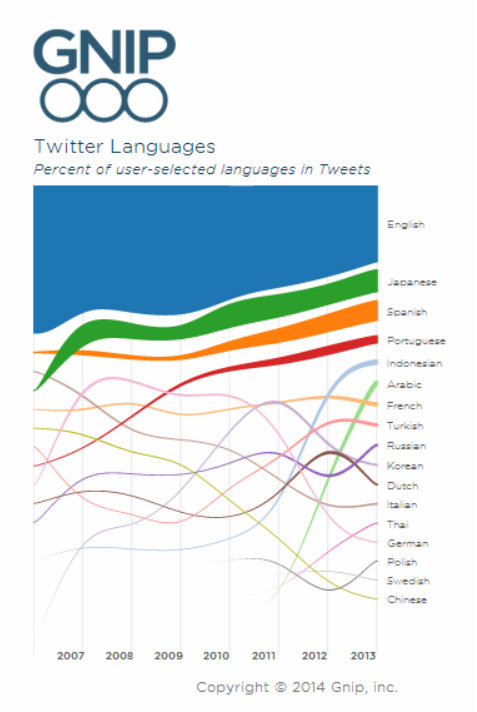
Photo source: Amnesty International
In the latest session of TechChange’s “Tech for International Crisis Response and Good Governance” class, I learned about the Panic Button, the emergency Android app recently launched by Amnesty International. The app is a step in the right direction for emergency alert applications, and may prove to be useful in other types of emergency situations. It was initially designed for activists working abroad, and essentially turns a cell phone into an alarm. While the app is running, the user can send pre-programmed SMS and GPS coordinates to three trusted contacts by hitting the phone’s power button multiple times. This simple process can be executed while the phone is located in the activist’s hand or pocket, and with minimal effort. With beta testing in 17 countries, this open source app was developed through an iterative process by networks of developers and activists, with two critical factors in mind: security and speed.
Pros. The speed of sounding an alarm is a major benefit of Panic Button, triggered by the power button on a user-friendly interface. This trigger allows users to be discreet in sending out an S.O.S. before their phone may be taken away by an adversary. Also, the GPS functionality provides trusted contacts with detailed information of where the person (or at least the phone) is located. This notification assumes that the activist has prepared ahead of time to both discuss with their contacts what to do in the event that an S.O.S. is received, and that they have turned the app on.
Cons. Security – particularly the interception of texts – remains a major concern. The app may reveal information about one’s location and contacts that could put all parties at increased risk. One of the major benefits of the app is sharing GPS coordinates, which need to be manually enabled. In an insecure environment, these may typically be switched off. The app needs to be switched on to work, which also means that the user needs to anticipate that they may be in a dangerous scenario – something very hard to do. These stipulations, as well as its learning curve, are potential stumbling blocks that need to be addressed.
Implications for sexual violence prevention. Despite these kinks, the Panic Button is a powerful tool. In its current state, Panic Button is specifically designed for activists, but its technology has the potential for use in other emergency situations, notably for women and girls at risk for sexual violence. Panic Button is similar to the award-winning and widely-used Circle of 6 app, but appears to be easier to use in an emergency situation. The ability to trigger Panic Button’s alarm without having to open the app itself is a critical differentiator and timesaver when an abduction or act of sexual aggression is occurring (similar to a scenario a Panic Button user would face). Circle of 6 is already being used in India, where not only sexual violence occurs on a far-too-frequent basis, but also where users are already comfortable using smart phones, and thus could also easily use Panic Button.
Panic Button is useful in environments that are dangerous and highly variable. With the open source nature of the app, one can only hope that the app will be adapted further to better address more specific challenges presented by additional contexts, and save both activists’ and women’s lives worldwide.
About Jessica Soklow
Jessica Soklow is working toward her Masters in International Affairs at George Washington University’s Elliott School and is alumna of TechChange’s “Tech for International Crisis Response and Good Governance” course. Her concentration at the Elliott School is on international development, with an emphasis on developing and implementing programming with a gender-specific lens. Jessica has conducted extensive research on gender-based violence in international contexts, with a specific focus on prevention mechanisms in both India and the United States. She is optimistic about how technology can be used in the future to help prevent violence on a global scale.
Learn about tools like Panic Button and other technology in our upcoming online course on Tech Tools & Skills for Emergency Management, which has an early bird discount that ends Oct 31!